Michelson Interferometer¶
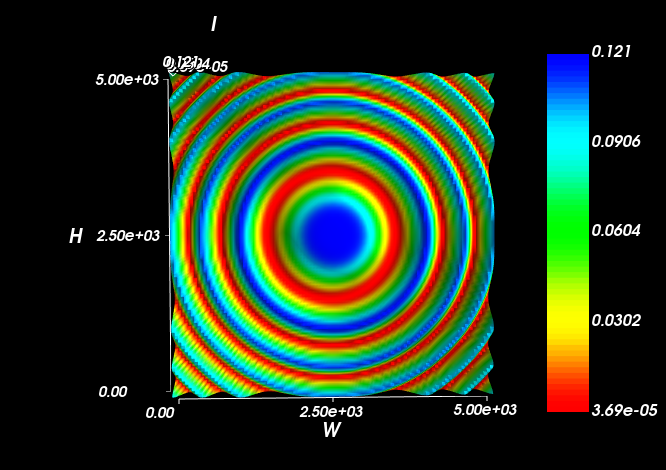
We can create a Michelson interferometer from a non-polarising beam-splitter and two mirrors. The second mirror has a spherical surface to generate a spherical wavefront at the detector-plane. The intensity distribution shows the classic Newton’s Rings type pattern.
from raypier.api import RayTraceModel, UnpolarisingBeamsplitterCube, CollimatedGaussletSource, CircleShape, GeneralLens,\
SphericalFace, PlanarFace, OpticalMaterial, PolarisingBeamsplitterCube, ParallelRaySource,\
GaussletCapturePlane, EFieldPlane, IntensitySurface
from raypier.intensity_image import IntensityImageView
src=CollimatedGaussletSource(origin=(-30,0,0),
direction=(1,0,0),
radius=5.0,
beam_waist=10.0,
resolution=10.0,
E_vector=(0,1,0),
wavelength=1.0,
display="wires",
opacity=0.05,
max_ray_len=50.0)
bs = UnpolarisingBeamsplitterCube(centre=(0,0,0),
size=10.0)
shape = CircleShape(radius=10.0)
f1 = PlanarFace(mirror=True)
f2 = SphericalFace(curvature=2000.0, mirror=True)
m1 = GeneralLens(name="Mirror 1",
shape=shape,
surfaces=[f1],
centre=(0,20,0),
direction=(0,-1,0))
m2 = GeneralLens(name="Mirror 2",
shape=shape,
surfaces=[f2],
centre=(20,0,0),
direction=(-1,0,0))
cap = GaussletCapturePlane(centre=(0,-20,0),
direction=(0,1,0))
field = EFieldPlane(centre=(0,-20,0),
direction=(0,1,0),
detector=cap,
align_detector=True,
width=5.0,
height=5.0,
size=100)
image = IntensityImageView(field_probe=field)
surf = IntensitySurface(field_probe=field)
model = RayTraceModel(optics=[bs, m1, m2],
sources=[src],
probes=[field, cap],
results=[image, surf])
model.configure_traits()
The rendered model looks as follows:
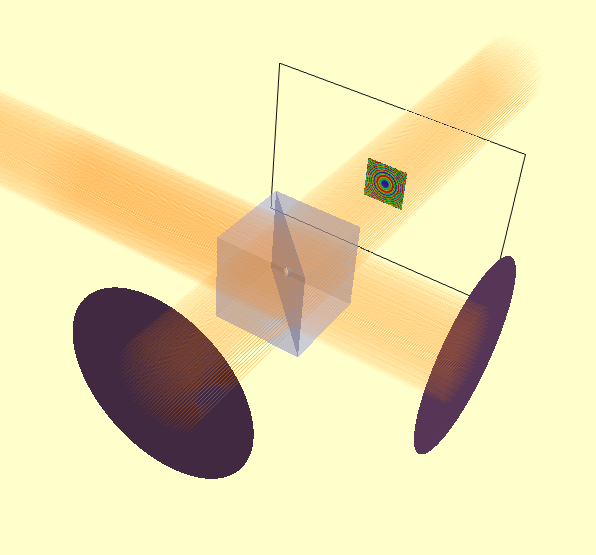
In this case, the E-field evaluation plane is large enough that we can see the intensity profile directly in the model.
However, viewing it in a IntensitySurfaceView is more convenient.